About data platform connections
dbt Cloud can connect with a variety of data platform providers including:
- AlloyDB
- Amazon Athena (Beta)
- Amazon Redshift
- Apache Spark
- Azure Synapse Analytics
- Databricks
- Google BigQuery
- Microsoft Fabric
- PostgreSQL
- Snowflake
- Starburst or Trino
You can connect to your database in dbt Cloud by clicking the gear in the top right and selecting Account Settings. From the Account Settings page, click + New Project.
These connection instructions provide the basic fields required for configuring a data platform connection in dbt Cloud. For more detailed guides, which include demo project data, read our Quickstart guides
Connection management
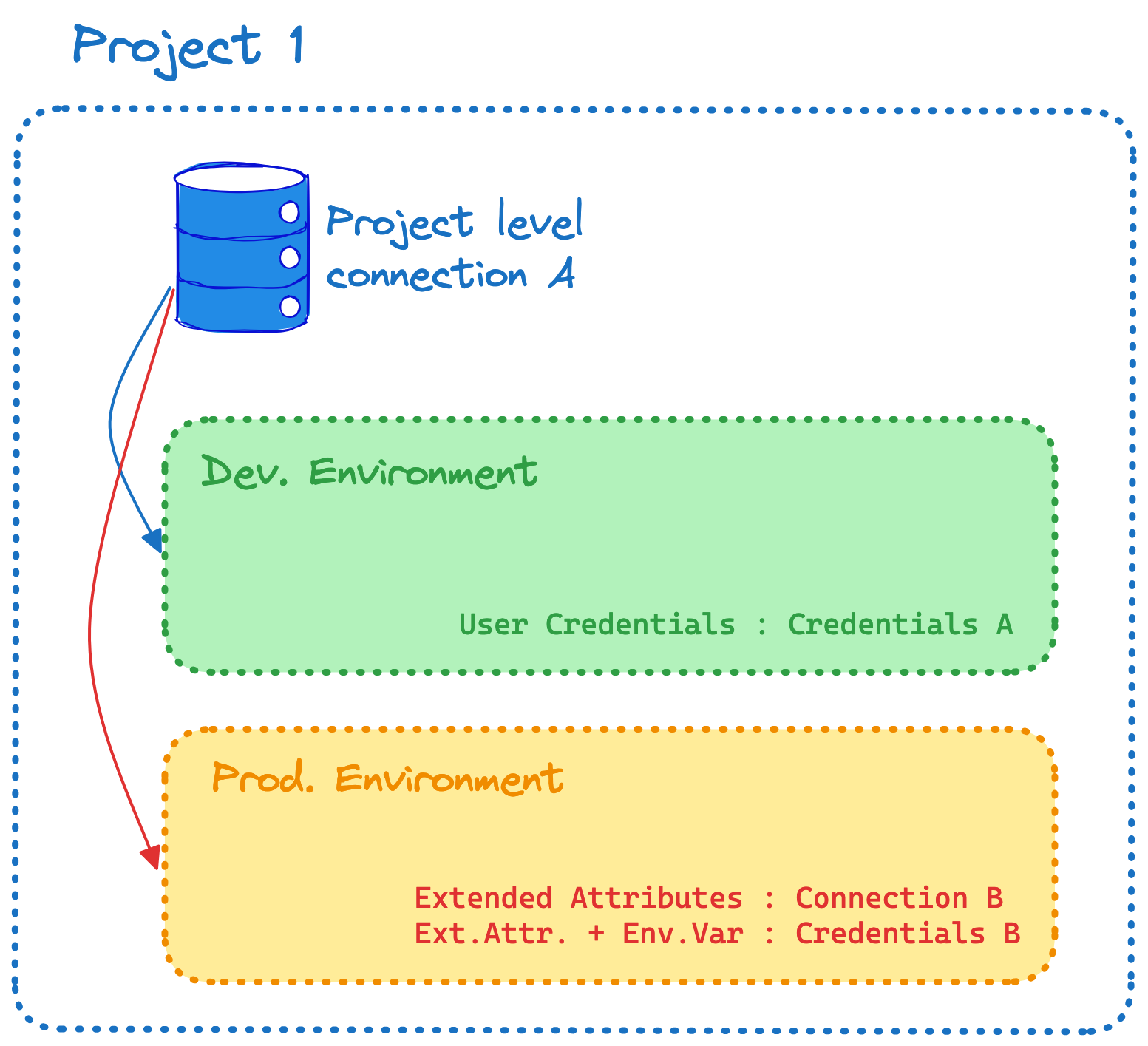
Starting July 2024, connection management has moved from the project level to the account level for all users in dbt Cloud. Previously, each dbt Cloud project could only have one connection, which was used across all its environments. Extended attributes were used to switch warehouse instances depending on the environment for a given project.
The following connection management section describes these changes.
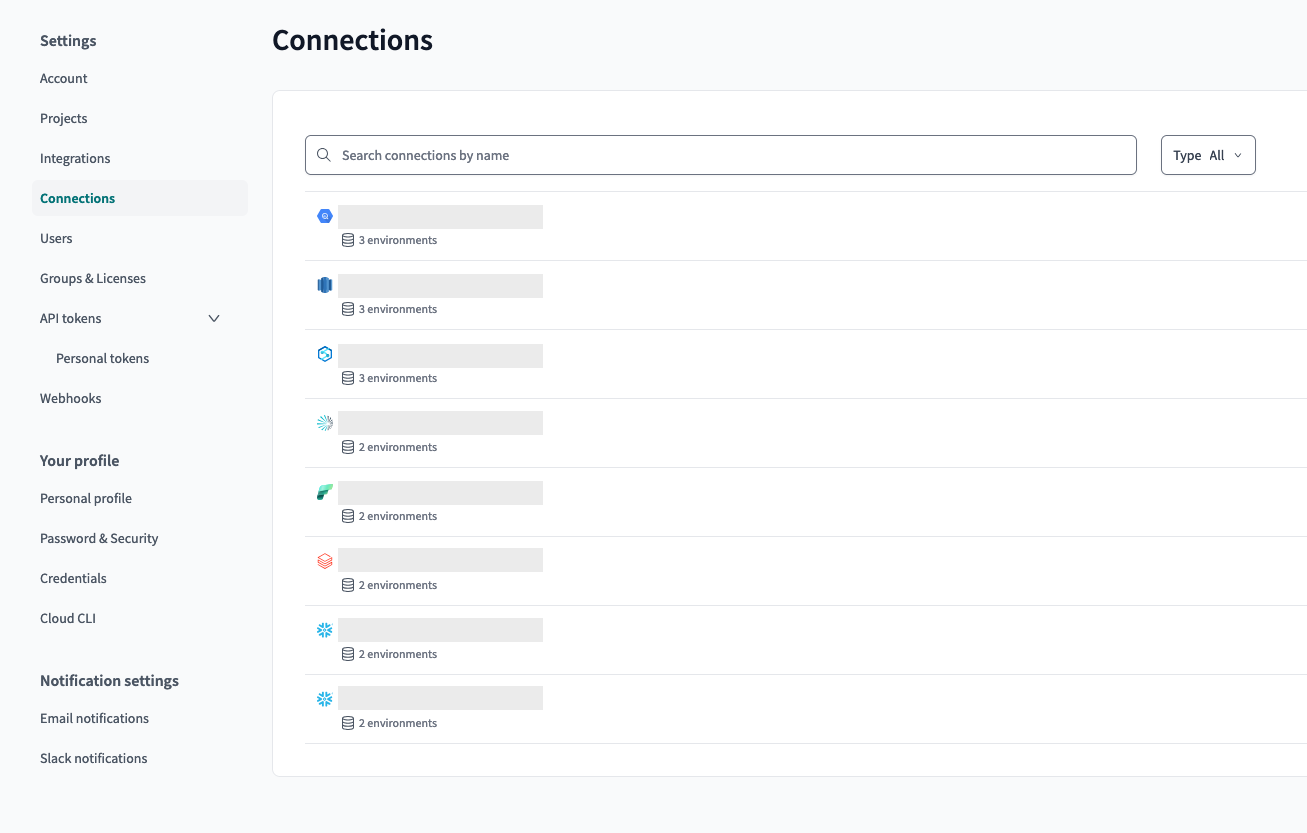
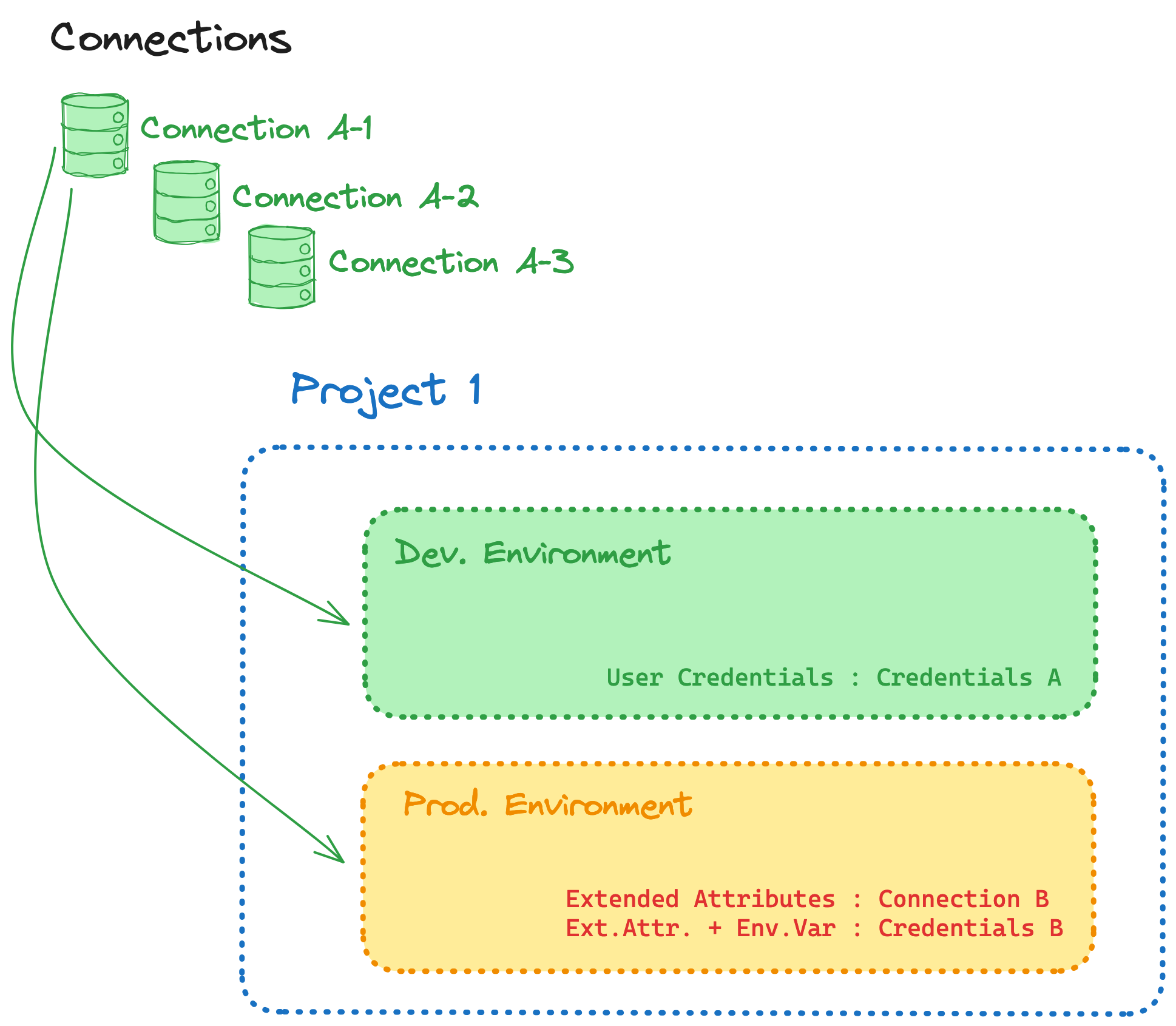
Warehouse connections are an account-level resource. As such you can find them under Accounts Settings > Connections:
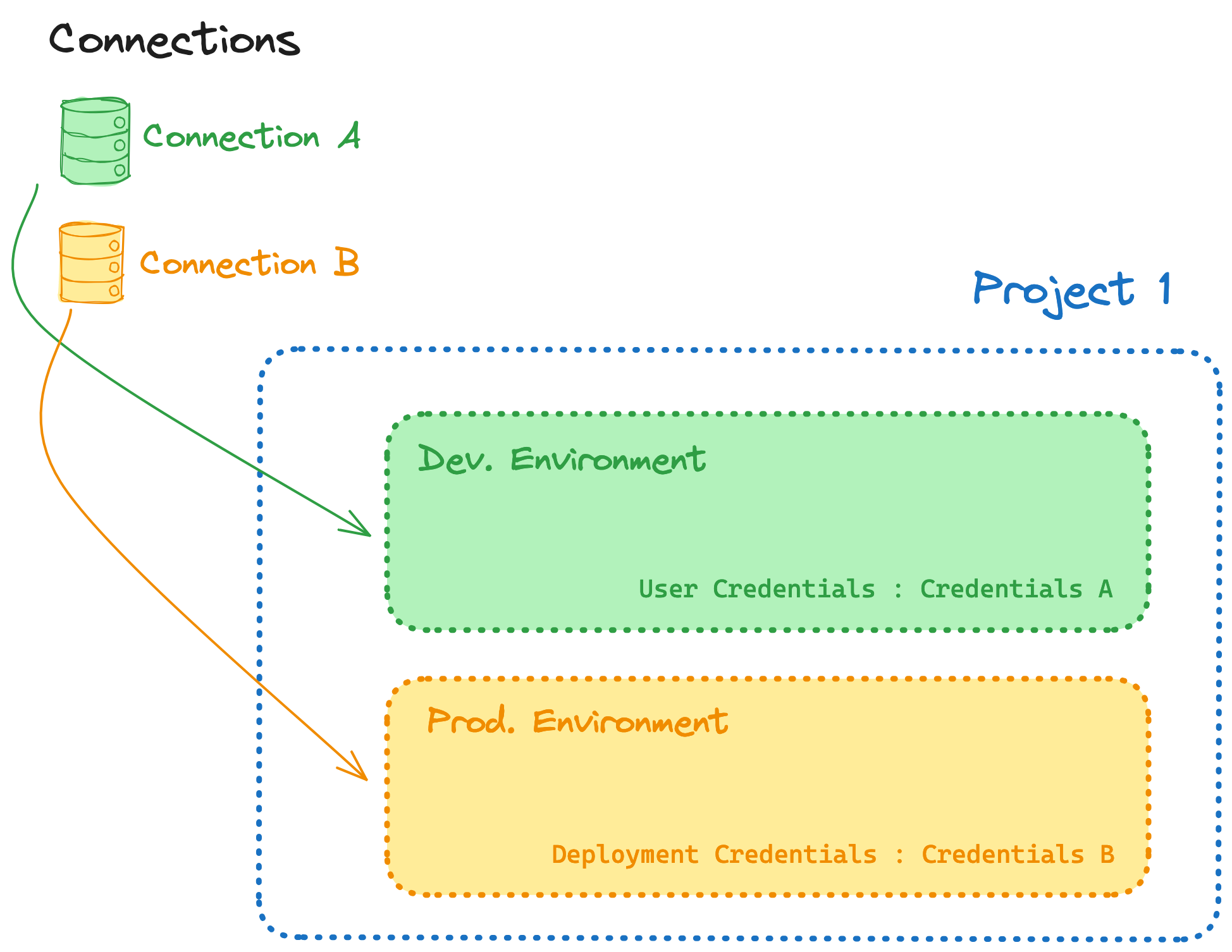
Warehouse connections can be re-used across projects. If multiple projects all connect to the same warehouse, you should re-use the same connection to streamline your management operations. Connections are assigned to a project via an environment.
As shown in the image, a project with 2 environments can target between 1 and 2 different connections. If you want to separate your production environment from your non-production environment, assign multiple connections to a single project.
Migration from project level connections to account level connections
Rolling out account-level connections will not require any interruption of service in your current usage (IDE, CLI, jobs, and so on.).
If your project did not previously have a development environment, you may be redirected to the project setup page. Your project is still intact. Choose a connection for your new development environment, and you can view all your environments again.
However, to fully utilize the value of account-level connections, you may have to rethink how you assign and use connections across projects and environments.
Please consider the following actions, as the steps you take will depend on the desired outcome.
- The initial clean-up of your connection list
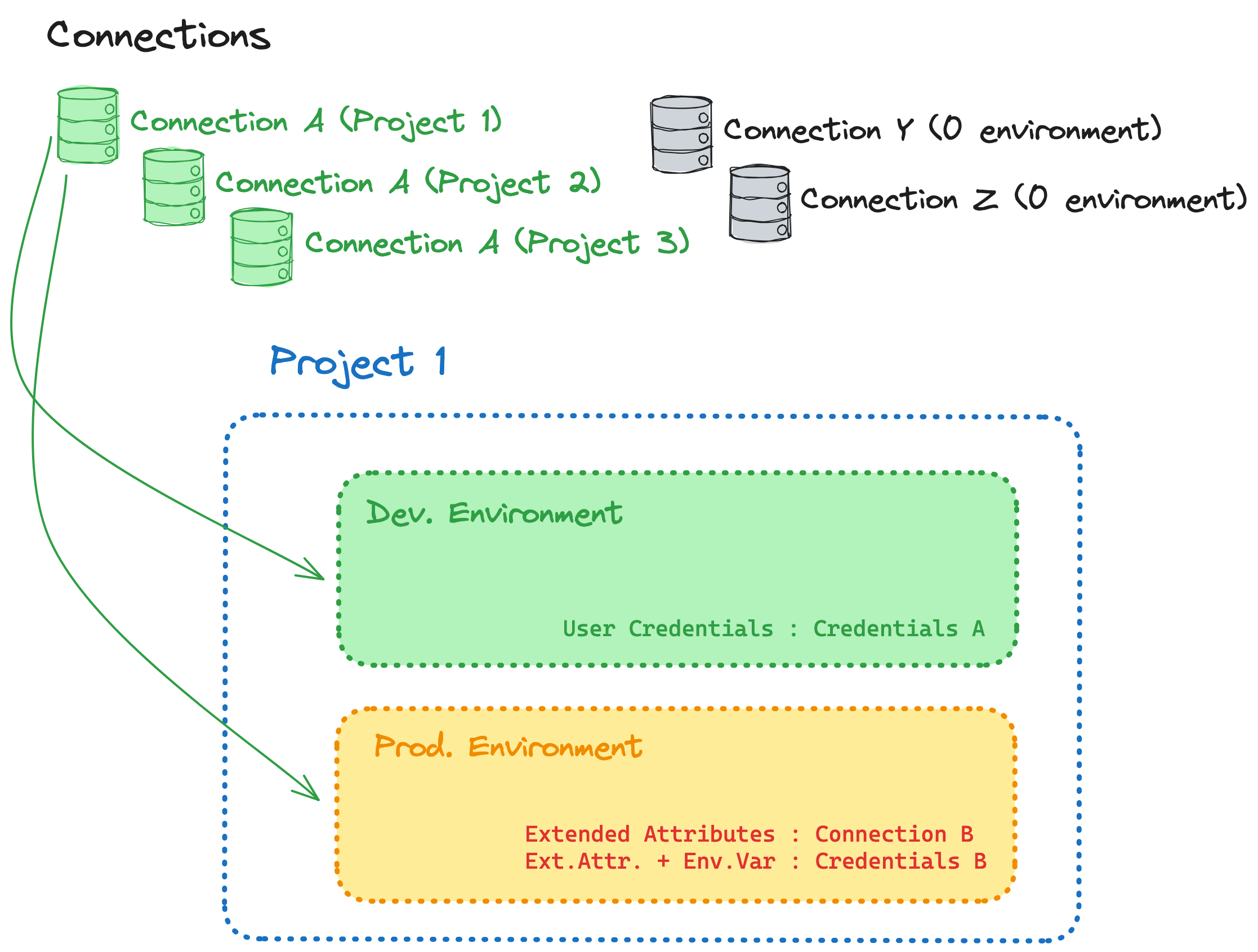
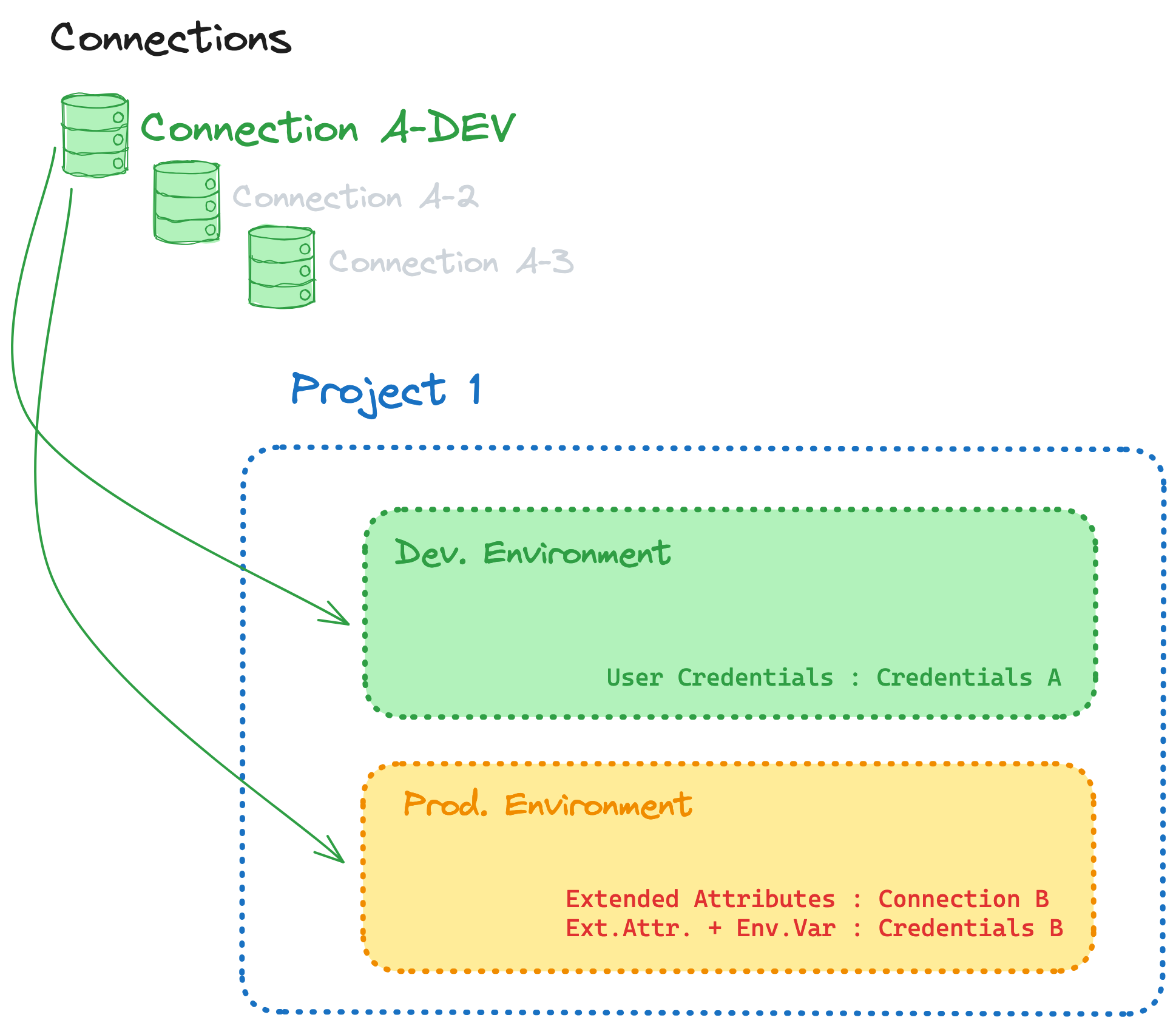
- Delete unused connections with 0 environments.
- Rename connections with a temporary, descriptive naming scheme to better understand where each is used
- Get granular with your connections
- Define an intent for each connection, usually a combination of warehouse/database instance, intended use (dev, prod, etc), and administrative surface (which teams/projects will need to collaborate on the connection)
- Aim to minimize the need for local overrides (like extended attributes)
- Come to a consensus on a naming convention. We recommend you name connections after the server hostname and distinct intent/domain/configuration. It will be easier to reuse connections across projects this way
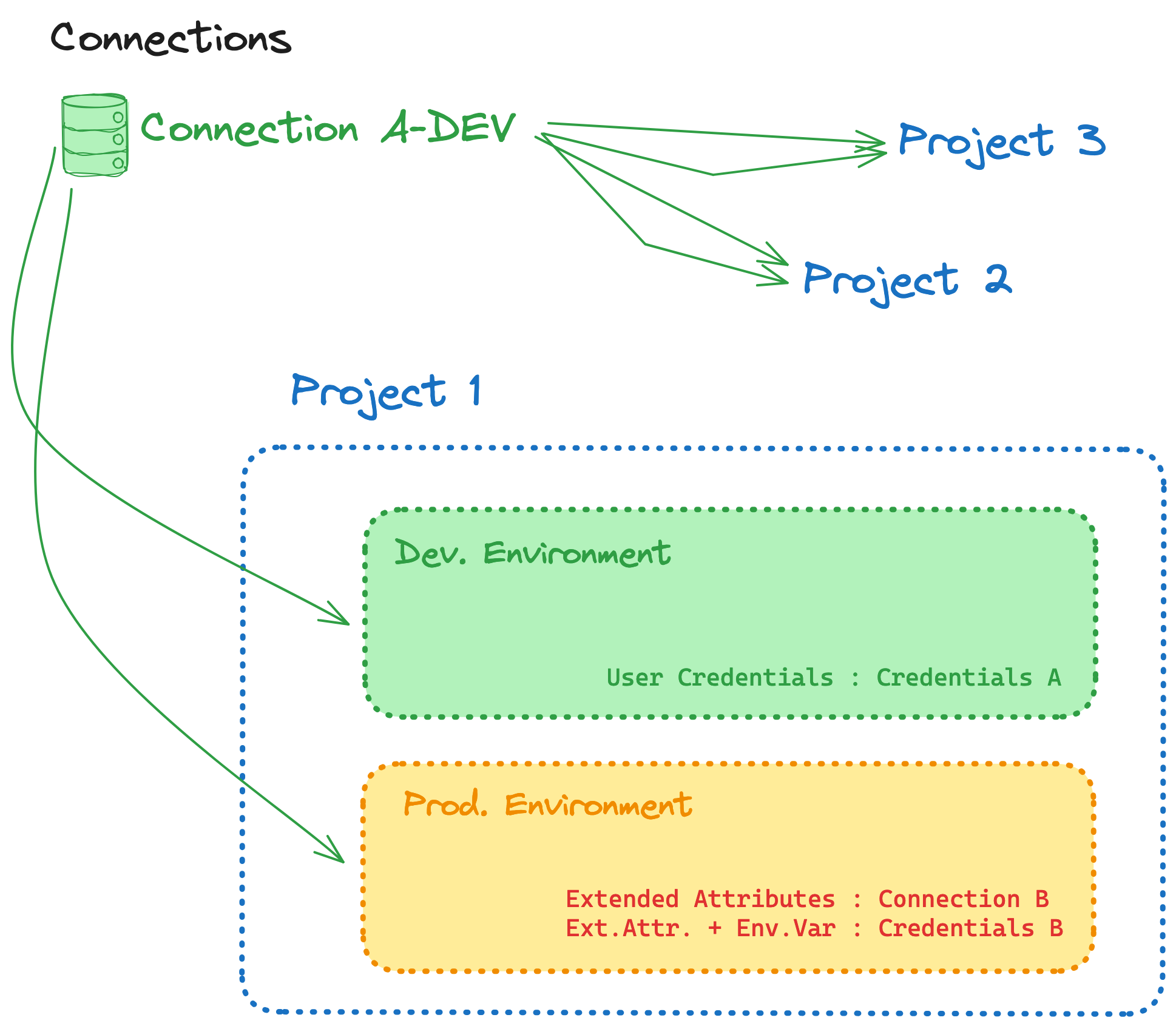
- Deduplication (connection list + environment details — not touching extended attributes for now)
- Based of the granularity of your connection details, determine which connections should remain among groups of duplicates, and update every relevant environment to leverage that connection
- Delete unused connections with 0 environments as you go
- Deduplicate thoughtfully. If you want connections to be maintained by two different groups of users, you may want to preserve two identical connections to the same warehouse so each can evolve as each group sees fit without impacting the other group
- Do not update extended attributes at this stage
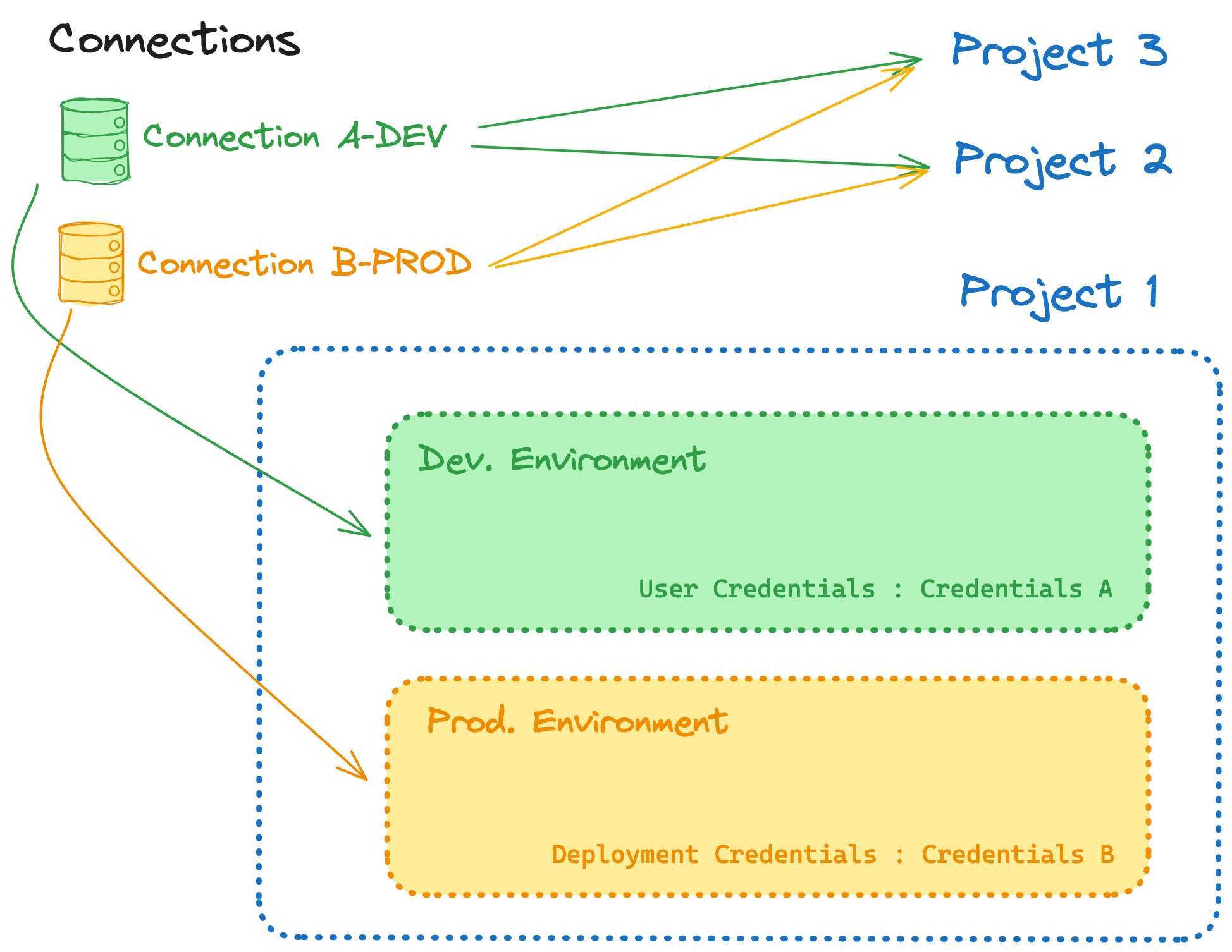
- Normalization
- Undertsand how new connections should be created to avoid local overrides. If you currently use extended attributes to override the warehouse instance in your production environment - you should instead create a new connection for that instance, and wire your production environment to it, removing the need for the local overrides
- Create new connections, update relevant environments to target these connections, removing now unecessary local overrides (which may not be all of them!)
- Test the new wiring by triggering jobs or starting IDE sessions
IP Restrictions
dbt Cloud will always connect to your data platform from the IP addresses specified in the Regions & IP addresses page.
Be sure to allow traffic from these IPs in your firewall, and include them in any database grants.
Allowing these IP addresses only enables the connection to your data warehouse. However, you might want to send API requests from your restricted network to the dbt Cloud API. For example, you could use the API to send a POST request that triggers a job to run. Using the dbt Cloud API requires that you allow the cloud.getdbt.com subdomain. For more on the dbt Cloud architecture, see Deployment architecture.